As a powerful chemical industry country, Japan currently ranks third in the world in terms of its total chemical output value. In 2008, the total output value of the Japanese chemical industry was 43.7 trillion yen, the industrial added value was 15.4 trillion yen, the number of employees in the industry reached 929,000, and the industrial increase per capita was 16.60 million yen. Japan’s chemical industry accounts for 13% of the country’s total manufacturing output, and the number of employees accounts for 11% of the total manufacturing industry. Japan's three largest chemical companies are among the world's top 500 companies. In 2009, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation ranked 14th in the world’s top 500 companies with sales revenue of US$ 16.74 billion, Sumitomo Chemical Company ranked No. 17 with US$ 13.12 billion, and Mitsui Chemicals Corporation ranked No. 18 with US$ 12.89 billion. In recent years, due to the lack of energy and resources in Japan, coupled with the intensification of international competition in the chemical industry, especially the rise of the chemical industry in emerging countries such as the Middle East, the Japanese chemical industry has encountered some new challenges, which has triggered a series of changes. Change 1: Increased energy resources constraints Japan is an island country with very limited resources. The domestic market is also very limited. In the process of chemical industry development, energy resources are increasingly constrained. Since energy resources are mostly dependent on imports, the relatively high prices have become a major factor restricting the development of their chemical industry. For example, the price of natural gas used by Saudi Arabia's Saab company is 0.75 US dollars / million British thermal units, while Japan's Mitsui Chemicals, Mitsubishi Chemical and other companies natural gas prices are 10 times that of Sabic. At the same time, the nuclear accident caused by the major earthquake on March 11, 2011 has a major impact on Japan’s energy supply pattern. Japan will rely more on thermal power and renewable energy to generate electricity. This will undoubtedly further increase the cost of electricity supply and increase consumption. The burden of bulk petrochemical products can reduce the market competitiveness of such products. Change 2: Decrease in Competitiveness of Basic Petrochemical Products Most ethylene plants in Japan were built and put into operation in the 1960s and 70s. In recent years, there have been only a few new installations. The average life span of the devices has reached 35 years, and the production capacity accounts for the global total production capacity. The proportion fell from 9.2% in 1990 to 5.3% in 2010. The average single set of production capacity was only 513,000 tons/year, while the average size of Saudi ethylene equipment was 1.032 million tons/year. Small-scale, outdated technology, and cracked raw materials are mainly high-priced naphtha. Compared with the new ethylene plants in the Middle East and China, the Japanese ethylene industry is losing its competitive advantage. Change 3: Environmental Climate Change as a Constraining Factor Japan has a relatively small land area and is surrounded by sea. It is a typical island nation. Environmental climate change has a great impact on Japan. Global warming has become one of the most concerned environmental issues in Japan. In particular, the chemical industry has attracted more and more attention from the ordinary Japanese people because of its high energy consumption, large emission, and toxic and hazardous substances. All parties have raised higher requirements for the safety production of chemical companies. The Japanese government complies with the requirements of social development, advocates environmental protection, and strengthens legislation on the safe production of chemical products. It requires companies to actively reduce CO2 emissions and publish chemical-related information. Against this background, the Japanese chemical industry actively took social responsibility and participated in related international activities. It creatively carried out a series of work in terms of ideas, systems and regulations, organizational structure, and work innovation, which not only created a great deal for the chemical industry. A good environment for development has established a good image of the industry, and it has also achieved great power in the international community and won wide respect.
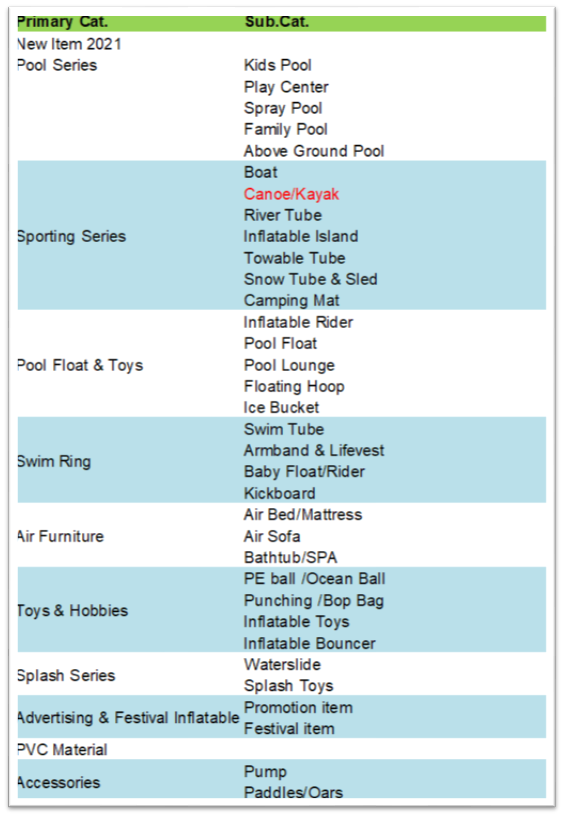
PD Toys plastic Co., Ltd is OEM & ODM manufacturer of inflatable products in the mainland of China with more 17 years of manufacturing experience. products ranges are Inflatable Toys, inflatable pools, inflatable pool floats, towable tubes, Air Furniture and Promotional Items etc. total have more than 1500 employees (4 factories) related to PVC inflatable products.
Operated under ISO 9001:2015 management system, We had passed factory Audit by Walmart, Taret, Disney ect, also passed all necessary certificates and testing such as ICTI, BSCI, SEMTA,Target FA, NBC Universal, FCCA, SGS, CVS Security, GSV, Disney FAMA ect. We have our own PVC raw materials manufacturing company, all the PVC we produced are compliance with European EN71, American ASTM standard and NON PHTHALATE (6P) standard.
Inflatable Waterslide,Water Slide,Inflatable Slip N Slide,Inflatable Slide P&D Plastic Manufacture Co., Ltd , https://www.jmairfuniture.com